Sometimes hidden in the shadows of passion are invisible dangers that raise of sexually transmitted diseases Infection, treatment and the effects on women and men and their health are the focus of this sensitive examination.
From hepatitis to HIV to HPV - the variety of sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) is large and their importance for pregnancy, birth and general sexual health should not be underestimated.
STDs – Don’t take them lightly

Photo by Ahmed Ashhaadh @jerryashhaadh, via Unsplash
In today's world, where freedom and openness around sexuality are increasing, it is crucial to be aware of the risks that unprotected sexual contact can pose.
Sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, HPV and HIV can have serious health consequences. Women in particular must consider the risk of transmission to the child if an infection goes untreated during pregnancy.
Hepatitis and other communicable diseases are no longer uncommon. Contraceptive methods do not provide complete protection against all infections.
Regular examinations are therefore essential in order to recognize symptoms early and initiate appropriate treatments. Prevention and education play an important role in the fight against the spread of sexually transmitted diseases in Germany.

Photo by Billie @billiebodybrand, via Unsplash
It is up to each individual to take responsibility and actively work towards their health.
Dramatic increase in the number of cases in Germany
Despite the largely stable HIV infection numbers in Germany (around 3,280 new cases in 2023), there is a worrying increase in other sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea, hepatitis B and chlamydia.
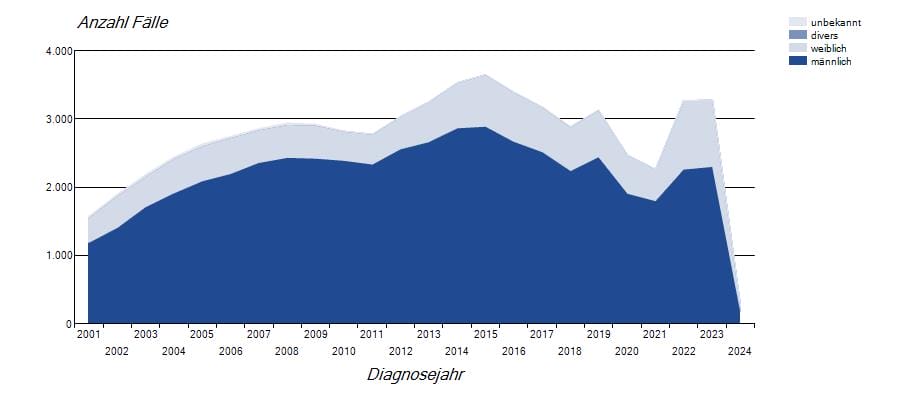
Data source: Robert Koch Institute - SurvStat@RKI 2.0, https://survstat.rki.de, query date: February 23, 2024
This trend is in clear contradiction to the goals of the United Nations, which want to end the HIV epidemic and combat other sexually transmitted diseases by 2030.
The increase in sexually transmitted infections (STIs ) in Germany is alarming, especially in light of medical advances in this area. According to the Robert Koch Institute, hepatitis B and around 300,000 people with chlamydia in 2022 , almost doubling compared to the previous year.
The number of new infections with syphilis - a supposedly cured disease from the Middle Ages - also reached a new record of 8,200 cases in 2023 (in comparison: 6,300 cases in 2021). Around 92% of these infections occurred in males.
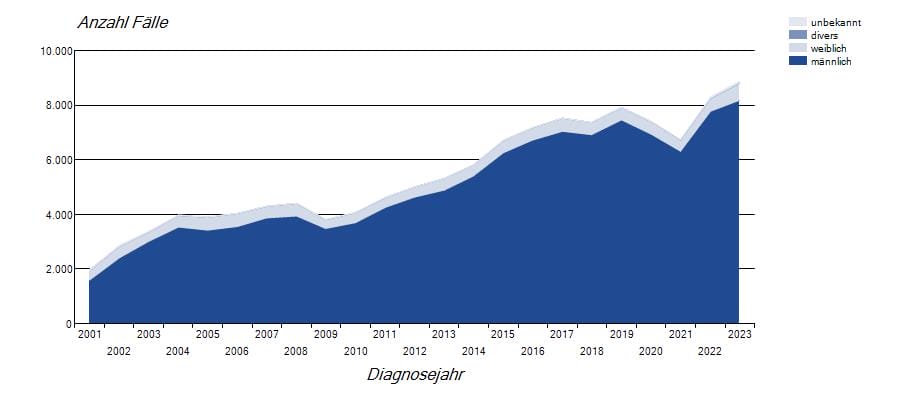
Data source: Robert Koch Institute - SurvStat@RKI 2.0, https://survstat.rki.de, query date: February 23, 2024
These figures clearly show that prevention and education measures are urgently needed to contain the spread of these infections. It is important that both the health system and the population as a whole are made aware of the risks of unprotected sexual intercourse and how to deal with sexually transmitted diseases.
Causes of the increase in sexually transmitted diseases in the German population
The reasons for the increase in sexually transmitted diseases in the population are diverse and complex.
A crucial factor is the lack of information about sexually transmitted infections, especially among young people. There is often a lack of awareness of the risks of unprotected sex and the importance of regular examinations.
Social taboos also play a role, which means that those affected do not seek treatment in a timely manner or do not inform their partners.
The use of contraceptives such as condoms is sometimes neglected, increasing the risk of infection.
trend towards multiple changing sexual partners also contributes to the spread of sexually transmitted diseases.
For all of these reasons, it is important to recognize these causes and take targeted preventative measures to counteract the increase in infections.
Prevention measures to avoid sexually transmitted diseases
Prevention is better than cure - especially in the case of communicable sexually transmitted diseases.
Prevention measures play a crucial role in preventing infections. Using condoms during sexual contact is an effective way to reduce the risk of infection. However, outdated ideas often still prevail among the population.
The statement “condoms protect” can no longer apply without reservation today, as many sexually transmitted infections can also be transmitted when condoms are used. Nevertheless, it is important to be aware that HIV is now very treatable.
People who have been diagnosed with HIV and are receiving appropriate therapy in which the viral load is below the detection limit can waive the mandatory wearing of condoms to prevent HIV infection. There are also ways for people without HIV to protect themselves.
prophylaxis (PrEP) offers an effective method of preventing infection with the HIV virus.
Regular medical examinations can detect and treat illnesses at an early stage.
Education in schools and the public is also essential to raise awareness of the dangers of unprotected sex.
Vaccination pathogens such as HPV can reduce the risk of infections.
Open communication with your partner about your own health status and previous sexually transmitted diseases is also important in order to take responsibility together and protect each other.

Photo by Vidar Nordli-Mathisen @vidarnm, via Unsplash
In the age of dating apps like Tinder or Grindr, sex has become quickly available - but our knowledge of sexually transmitted infections often lags behind. In order to remedy this and provide information, Y-Kollektiv reporter Julia Rehkopf obtained an update: She spoke to a person affected by HIV, a patient with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), a doctor and representatives of the health department.
Prevention begins with each individual and contributes significantly to reducing the spread of sexually transmitted diseases.
Treatment options for diagnosed sexually transmitted diseases
Unfortunately, sexually transmitted diseases are not uncommon and can have serious consequences. But what happens if an infection is diagnosed?
Treatment options for sexually transmitted diseases vary depending on the type of disease and individual circumstances. It is crucial that those affected seek medical advice quickly in order to receive the right treatment.
From antibiotics to treat syphilis to antiviral drugs for HIV, modern medicine offers various ways to combat these infections.
The importance of regular checkups and tests
Nowadays it is more important than ever to have regular check-ups and tests for sexually transmitted diseases. Infections often have no noticeable symptoms, which means they can go unnoticed.
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, especially with communicable diseases such as HPV or HIV.
Women should be tested for infections, especially during pregnancy, to avoid complications during childbirth.
Hepatitis and syphilis are other sexually transmitted diseases that can often have serious consequences. Testing yourself regularly is an important step in your own health care and in preventing further infections in the population.
Educational work and raising public awareness
Educating and raising public awareness about sexually transmitted diseases plays a crucial role in containing these infections.
It is important that information about transmission routes, symptoms and prevention measures be widely disseminated to raise awareness of the risks.
Through targeted campaigns and education initiatives, people can be encouraged to get regularly tested for STDs and have open conversations about sexual health
Dealing openly with the topic can help reduce prejudices and make it easier for those affected to access important information.
Frequently asked questions on the topic will be answered shortly
What are the 5 most common sexually transmitted diseases?
The five most common sexually transmitted diseases are chlamydia , gonorrhea (gonorrhea) , syphilis , genital warts (HPV) and genital herpes .
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that can cause inflammation in the genital area.
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and can lead to inflammation of the genital organs.
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that progresses through multiple stages and can cause serious health problems if left untreated.
Genital warts are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) and can lead to warts in the genital area. Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus and manifests itself as painful blisters in the genital area.
It is important to see a doctor if you suspect a sexually transmitted disease to receive appropriate treatment and prevent the infection from spreading.
How do I know if I have sexually transmitted diseases?
It is important to note that many STDs do not show any obvious symptoms . If you sexually active and have concerns, you should consult a doctor. A doctor can perform tests to determine whether you have a sexually transmitted disease.
Typical tests include blood tests, urine tests or swabs. Some signs of STDs may include itching, burning during urination, unusual discharge, or rashes in the genital area.
You can also get help and support with examinations for sexually transmitted diseases from Deutsche Aidshilfe .
It is important to have regular exams and learn about safe sexual practices to minimize the risk of sexually transmitted diseases.
Remember that there is no shame in seeking help and your health comes first.
How do you know you have chlamydia?
Chlamydia infections can often be asymptomatic, which makes them particularly dangerous because they can lead to serious complications if left untreated. When signs do occur, they are different in men and women. Men may experience symptoms such as burning during urination, discharge from the penis, and pain in the scrotum.
In women, signs of chlamydia infection include unusual discharge, painful urination, painful intercourse, and abdominal pain.
In some cases, breakthrough bleeding or bleeding after intercourse may occur. It's important to note that most people with chlamydia have no symptoms, which is why regular testing for sexually transmitted infections is recommended.
If you suspect you have chlamydia or have risk factors for it, you should be examined by a doctor immediately.

